How do solar panels work?
time:2023-06-14 14:52:24 Views:0 author:Jinan Freakin Power Ltd.
Solar panels, also known as PV panels, transform sunlight into electrical power. The quantity of sunshine reaching the Earth's surface in an hour and a half is sufficient to supply our planet's energy requirements for a whole year, as reported by the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy.

Photons are found in sunlight, which is a form of electromagnetic radiation. When sunlight radiates to the Earth and onto a solar panel, the energy is absorbed.
When sunlight hits the cells, it causes a flow of electrons, which generates an electric current. This current is then collected by wires on the panels and sent to an inverter, which converts it from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).
The AC electricity produced by the solar panels is then used to power homes or businesses. Any excess electricity generated can be stored in batteries for later use, or sent back to the grid for credit through a process called net metering.
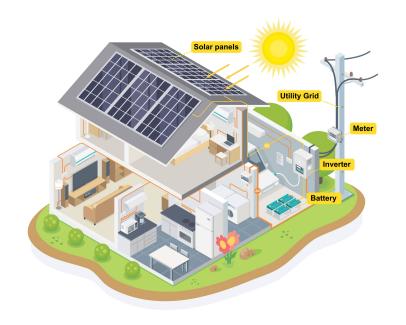
The amount of electricity generated is dependent on how many cells are in each panel: The more PV cells, the more electricity.
Overall, solar panels offer a clean, renewable energy source that is becoming increasingly popular and accessible as technology improves and costs come down.